
Revision Questions on Current and Potential Difference (1)Wherever you see an input box in the following text, please fill in the correct words or numbers (to 2 d.p. where appropriate). You might well need a calculator to do this, so here are some links to a few online calculators. They all open up in new tabs, and at least one of them should work! https://www.calculator.net/scientific-calculator.html |
 A student wants to investigate how the current through a filament lamp affects its resistance. She has access to the following components: 12 volt battery, filament lamp, variable resistor, voltmeter, ammeter.
A student wants to investigate how the current through a filament lamp affects its resistance. She has access to the following components: 12 volt battery, filament lamp, variable resistor, voltmeter, ammeter.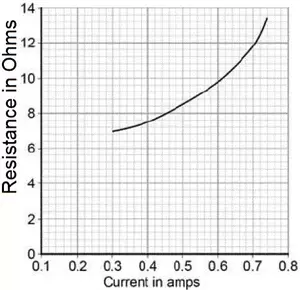 Describe how the student could use his circuit to investigate how the current through a filament lamp affects its resistance. [4 marks]
Describe how the student could use his circuit to investigate how the current through a filament lamp affects its resistance. [4 marks]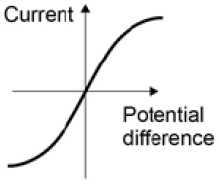
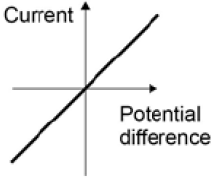
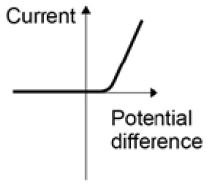
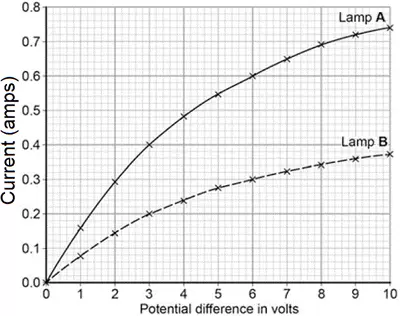 A student investigated how current varies with potential difference for two different lamps. His results are shown in the graph.
A student investigated how current varies with potential difference for two different lamps. His results are shown in the graph.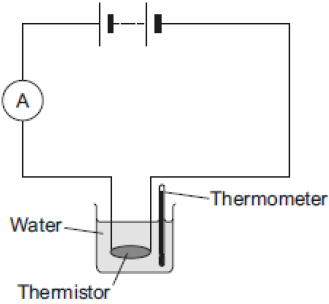 The diagram on the right shows the apparatus used to investigate how the current through a thermistor depends on the temperature of the thermistor.
The diagram on the right shows the apparatus used to investigate how the current through a thermistor depends on the temperature of the thermistor.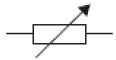 B.
B. 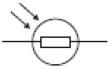 C.
C. 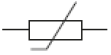
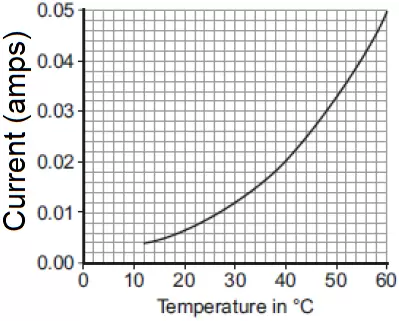
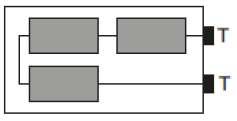 The diagram on the right shows the inside of a battery pack designed to hold three identical 1.5 V cells.
The diagram on the right shows the inside of a battery pack designed to hold three identical 1.5 V cells. B.
B.  C.
C.  D.
D. 
 The circuit on the right shows a variable resistor and a fixed value resistor connected in series in a circuit. Explain how an ammeter might be connected to measure the current in the circuit. [1 mark]
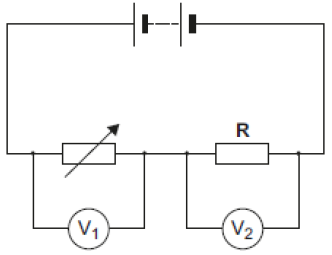
The circuit on the right shows a variable resistor and a fixed value resistor connected in series in a circuit. Explain how an ammeter might be connected to measure the current in the circuit. [1 mark]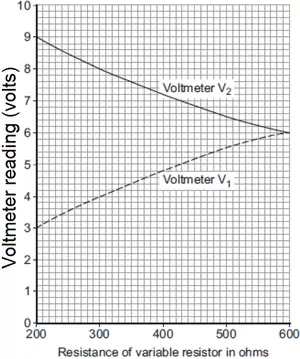 The graph on the right shows how the reading on voltmeter V1 and the reading on voltmeter V2 change as the resistance of the variable resistor changes. Calculate the potential difference of the battery:
Volts.
The graph on the right shows how the reading on voltmeter V1 and the reading on voltmeter V2 change as the resistance of the variable resistor changes. Calculate the potential difference of the battery:
Volts.
 The diagram on the right shows a three-pin plug.
The diagram on the right shows a three-pin plug.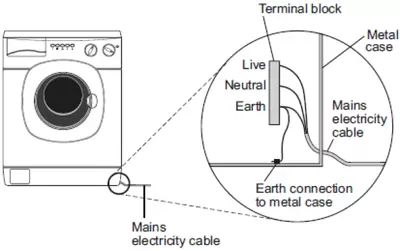 The digram on the right shows how the mains electricity cable is connected to the washing machine. The earth wire is connected to the metal case of the washing machine. If a fault makes the metal case live, the earth wire and fuse inside the plug prevent the mains cable from overheating and causing a fire. Explain how. [2 marks]
The digram on the right shows how the mains electricity cable is connected to the washing machine. The earth wire is connected to the metal case of the washing machine. If a fault makes the metal case live, the earth wire and fuse inside the plug prevent the mains cable from overheating and causing a fire. Explain how. [2 marks]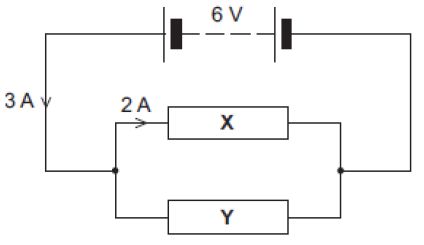
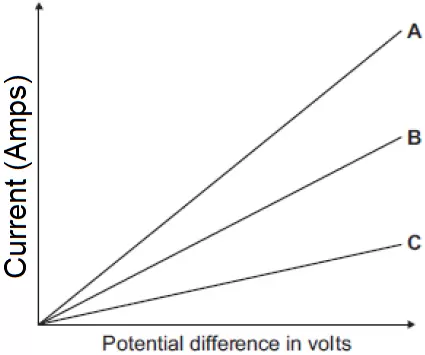 The graph on the right shows the current−potential difference graph for three wires, A, B and C.
The graph on the right shows the current−potential difference graph for three wires, A, B and C.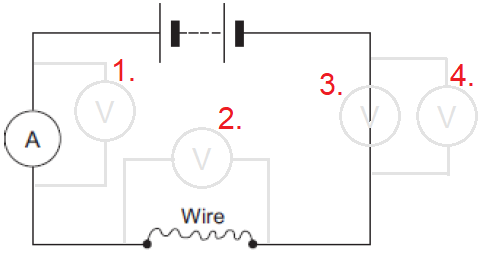 A student looked at the data in the table and wrote this conclusion: "The resistance of a wire depends on the type of metal from which the wire is made." The student could not be certain that her conclusion is true for all types of metal. Suggest what extra data is needed for the student to be more certain that the conclusion is correct. [1 mark]
A student looked at the data in the table and wrote this conclusion: "The resistance of a wire depends on the type of metal from which the wire is made." The student could not be certain that her conclusion is true for all types of metal. Suggest what extra data is needed for the student to be more certain that the conclusion is correct. [1 mark]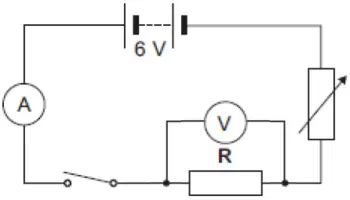 A student uses the circuit shown to measure the resistance of resistor R.
A student uses the circuit shown to measure the resistance of resistor R.